WHITE FOx uses fiber-optic dip-in biosensors to directly measure an analyte of interest from unporified samples such as blood, cell lysates and periplasmic extracts. Providing accurate results from a range of sample inputs demonstrates the robustness and versatility of the fiber-optic biosensor technology.
- Serum
- Plasma
- Whole blood
- Cell supernatant
- Cell lysate
- Periplasmic extracts
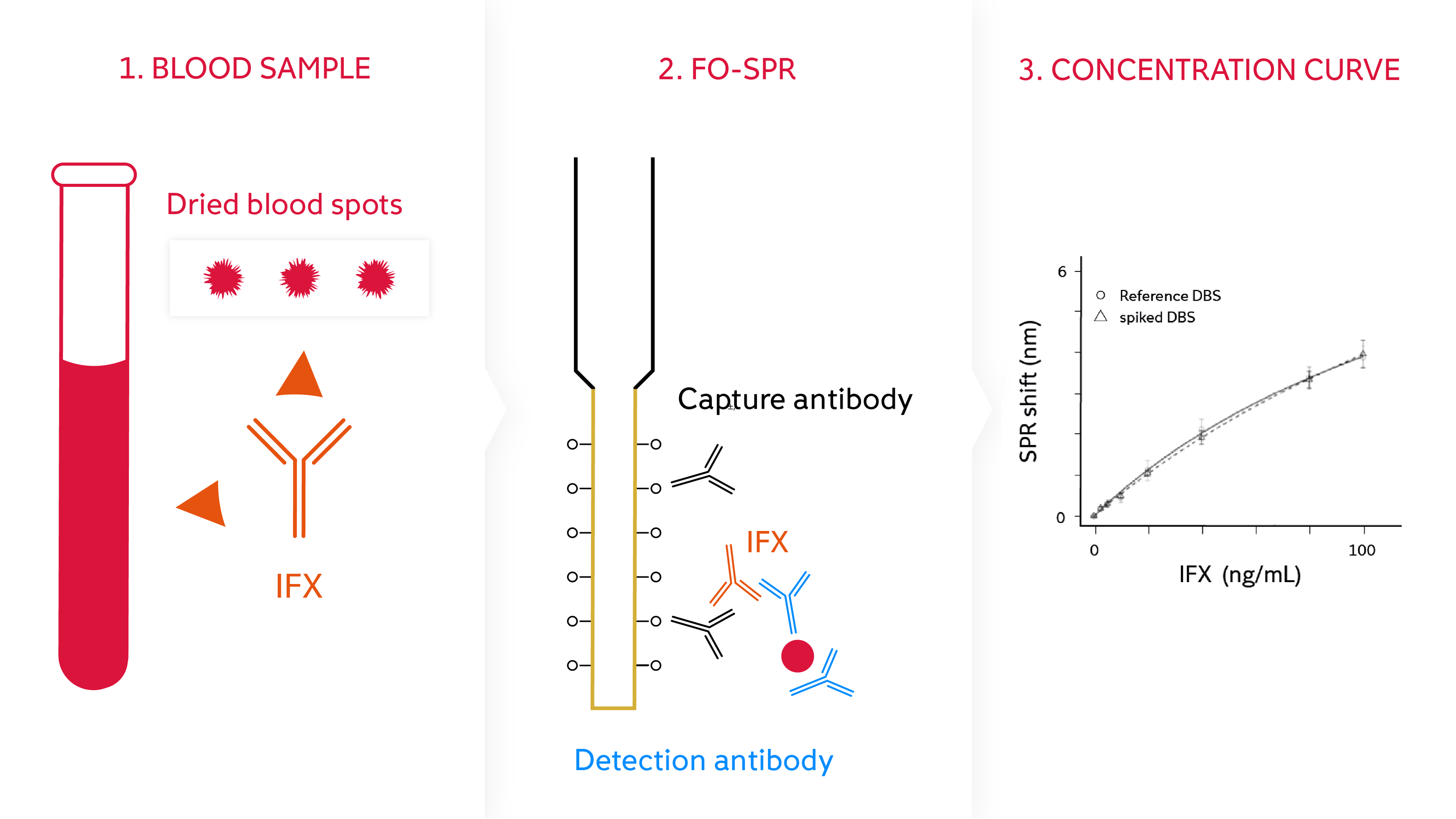
Case study: Dry blood spot sampling
Dry blood spots are an ideal method for patients to provide blood samples from home, with minimal transportation requirements. However, blood cell bursting, and the altered structure of analytes caused by the drying process, can influence the detection efficiency.
In tests with infliximab (IFX), a monoclonal antibody used for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease, the WHITE FOx bioassay demonstrated that:
- The blood drying process did not affect analyte extraction or interfere with the bioassay antibodies.
- IFX was uniformly distributed across the blood spot on the paper.
- Non-specific binding due to blood cell bursting did not interfere with the fiver-optic bioassay.
Case study: Detecting a tumor protein in serum using gold nanoparticle sandwich amplification
The Pharmacology Department at the University of Cambridge are investigating a potential biomarker to detect triple negative breast cancer tumors in blood serum. Traditional technologies (ELISA, mass spectroscopy and conventional SPR) had proven unsuitable for their purposes, so they looked to the WHITE FOxTM for an alternative method.
WHITE FOx fiber-optic sensors with gold nanoparticle signal amplification matched or improved on the detection sensitivity over existing SPR technology. This allowed the development of a test suitable to retrospectively test patient samples for the candidate biomarker.
Relevant publications
Page 1 of 1
App Note: AN1 Looking for a faster way to monitor biotherapeutics yield from cell culture?
More efficient drug discovery and R&D using a dip-in assay WHITE FOx can be used on crude samples, including cell culture media, and could be invaluable as an analysis tool...
May 14, 2024
White paper: WP9 Isolation of neuron-specific extracellular vesicles from human plasma using FO-SPR
White paper 9 | Version 2 | Tobias Zbik, Filip Delport SUMMARY Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are an increasingly popular target in the search for novel biomarkers in the field of...
January 25, 2024
Measuring ADAMTS-13 activity to diagnose thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: a novel, fast fiber-optic surface plasmon resonance immunoassay
Bonnez et al. (2023) RPTH 7, DOI: 10.1016/j.rpth.2023.102171 Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) is characterized by severe ADAMTS-13 activity deficiency (<10%). Diagnostic testing is challenging because of unavailability, high cost, and…
September 27, 2023
Detection of Breast Cancer-Specific Extracellular Vesicles with Fiber-Optic SPR Biosensor
Yildizhan et al. (2023) International Journal of Molecular Sciences DOI: 10.3390/ijms24043764 Extracellular vesicles (EVs) have attracted great attention as potential biomarkers for cancer diagnostics. Although several technologies have been developed…
February 15, 2023
Immunogenic affinity and extracellular vesicle quantification in blood with FO-SPR
June 20-22, 2022 – MOSBRI Scientific Conference Our CTO, Dr. Filip Delport, had the opportunity to present at the 1st MOSBRI Scientific Conference in June 2022. He explained how the…
December 8, 2022
Innovative FO-SPR Label-free Strategy for Detecting Anti-RBD Antibodies in COVID-19 Patient Serum and Whole Blood
Qu et al. (2022) ACS Sensors DOI: 10.1021/acssensors.1c02215 The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has emphasized the urgent need for rapid, accurate, and large-scale diagnostic tools. Next to this, the significance of…
January 27, 2022
White paper: WP5 Extracellular vesicle quantification in complex matrices
White paper 5 | Version 2 | Kris Ver Donck, Filip Delport, Kim Stevens Based on original publication: Yildizhan et al. (2021) Journal of Extracellular Vesicles. 10 (4) ABSTRACT Fiber-optic...
December 15, 2021
White paper: WP3 Sensitive protein quantification in whole blood, dried blood spots, serum and plasma
White paper 3 | Version 2 | Kim Stevens, Kris Ver Donck, Filip Delport Based on original publication: Lu et al. (2017) Analytical Chemistry 89, 3664-3671. (1) ABSTRACT Fiber-optic surface...
June 29, 2021
White paper: WP2 sensitive protein quantification in serum – comparison of FO-SPR and ELISA
White paper 2 | Kim Stevens, Kris Ver Donck, Filip Delport Based on original publication: Lu et al. (2016) Biosensors and Bioelectronics 79, 173–179. (1) ABSTRACT This white paper demonstrates...
April 23, 2021
WHITE FOxTM technical specifications
You can find the technical specifications of the White FOxTM here: DOWNLOAD
April 8, 2021
FO-SPR biosensor calibrated with recombinant extracellular vesicles enables specific and sensitive detection directly in complex matrices
Yilidzhan et al. (2021) J. Extracell. Vesicles 10 Extracellular vesicles (EVs) have drawn huge attention for diagnosing myriad of diseases, including cancer. However, the EV detection and analyses procedures…
February 23, 2021
Immunoassay for detection of infliximab in whole blood using a fiber-optic surface plasmon resonance biosensor
Lu et al. (2017) Anal. Chem. 89, 3664−3671 Monitoring the concentration of a therapeutic drug antibody, infliximab (IFX), is recommended for enhancing its efficacy in patients with inflammatory bowel…
February 22, 2017
Competitive inhibition assay for the detection of progesterone in dairy milk using a fiber optic SPR biosensor
Daems et al. (2017) Analytica Chimica Acta 950, 1e6 Analytical methods that are often used for the quantification of progesterone in bovine milk include immunoassays and chromatographic techniques. Depending on the selected method,…
January 15, 2017
Fiber optic-SPR platform for fast and sensitive infliximab detection in serum of inflammatory bowel disease patients
Lu et al. (2016) Biosensors and Bioelectronics 79, 173–179 Infliximab (IFX) is a therapeutic monoclonal antibody used for treating patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). In order to improve…
May 15, 2016
Page 1 of 1
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.