WHITE FOx’s dip-in probe format allows rapid and robust analyses of phage display libraries. Our system allows users to easily monitor biopanning where phage are identified based on displayed peptides that bind to a given target.
WHITE FOx was designed with ease of use at its core and allows you to streamline the study of affinity and binding kinetics of proteins on large particles, such as viruses, phage, cells, and microvesicles.
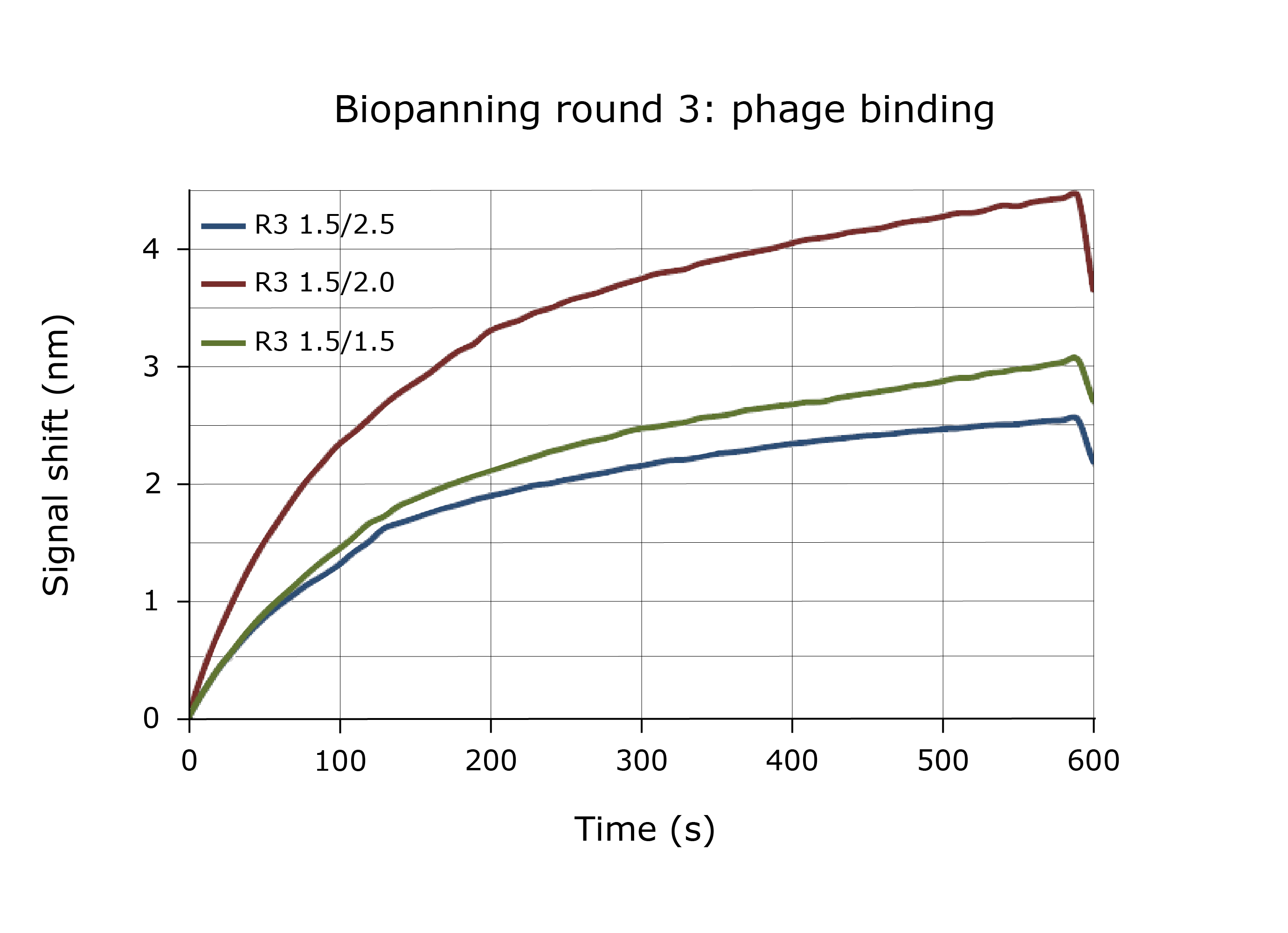
Case study: Real-time analysis of phage display libraries
WHITE FOx measures the real-time concentration of phage clones through multiple cycles of selection.
- Measure directly in culture media with limited sample preparation.
- Fast selection of strongly binding polyclonal cultures with data in approximately 30 minutes from sampling.
- Integrate with existing biopanning workflows.
Binding curves generated from the third round of biopanning
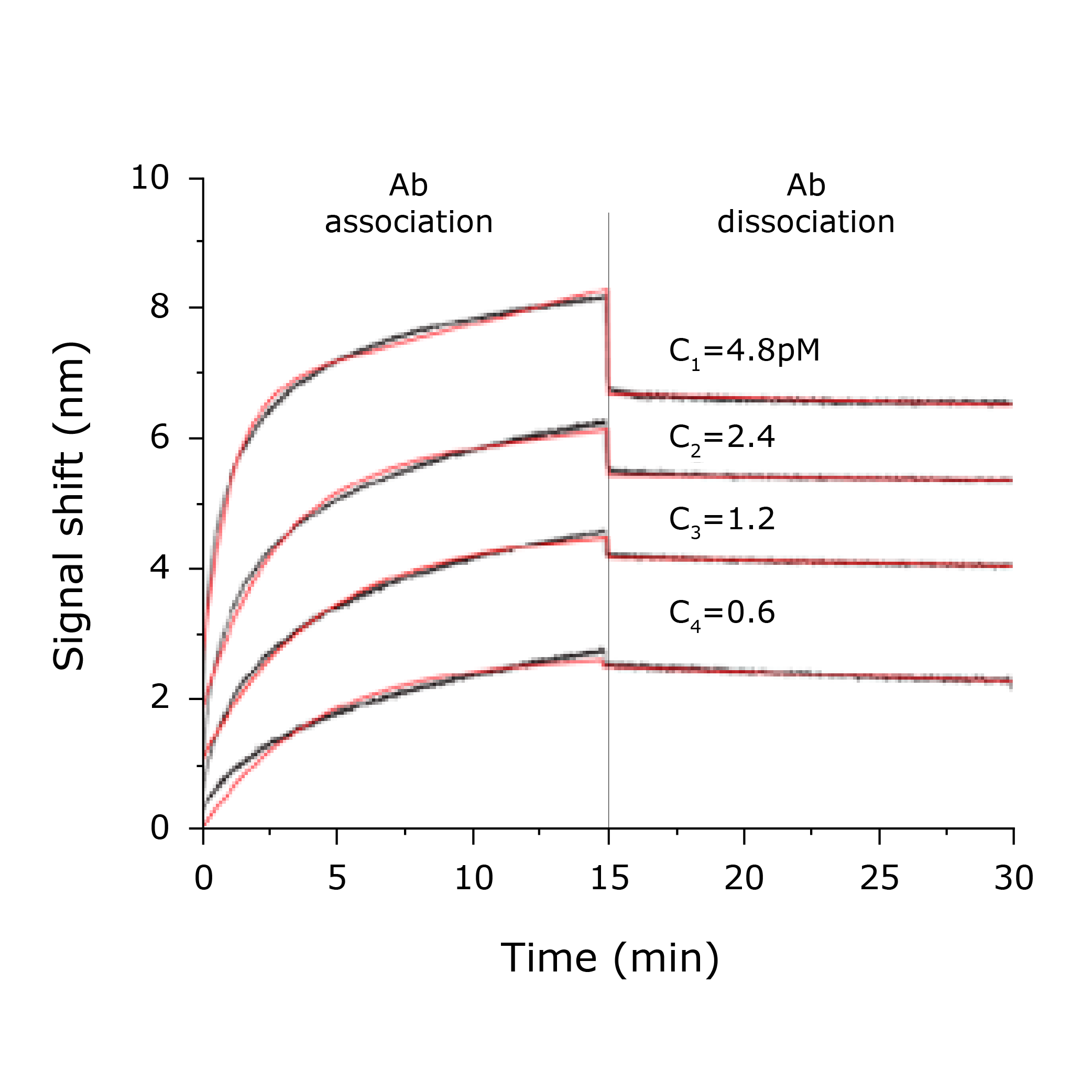
Case study:
Phage kinetic affinity analysis
WHITE FOx allows the study of affinity and binding kinetics of phage-displaying peptide libraries in a microfluidic-free, dip-in experiment with a clear correlation between binding parameters and the expression of the target protein.
- Label-free kinetic characterization directly on monoclonal phage.
- Wide range of affinity from picomolar to nanomolar.
- Individual determination of kon, koff and kD.
- Distinguishes binding affinity that end-point-based ELISA could miss.
- Only 30 minutes to results. No purification, skip cleaving.
Relevant publications
Page 1 of 1
App Note: AN3 Improve your biopanning selection process with real-time monitoring
More efficient biotherapeutic discovery and screening using a fast, dip-in assay WHITE FOx can measure the real-time concentration of phage clones through multiple cycles of selection. The dipin sensor configuration...
May 14, 2024
App Note: AN2 Can you get immediate kinetic characterization from phage display clones?
More efficient biotherapeutic discovery and screening using a fast, dip-in assay WHITE FOx can measure the kinetics of phage clones to provide insights into their affinity and avidity, providing a...
White paper: WP6 Using FO-SPR to select for nanobodies in phage display
White paper 6 | Version 2 | Kris Ver Donck, Dagmara Minczakiewicz, Filip Delport, Kim Stevens Based on original publication: Knez et al. (2013) Analytical Chemistry 85, 10075 - 10082...
April 29, 2022
Affinity comparison of p3 and p8 peptide displaying bacteriophages using surface plasmon resonance
Knez et al. (2013) Anal. Chem. 85, 10075−10082 Ever increasing demands in sensitivity and specificity of biosensors have recently established a trend toward the use of multivalent bioreceptors. This…
September 30, 2013
Page 1 of 1
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.