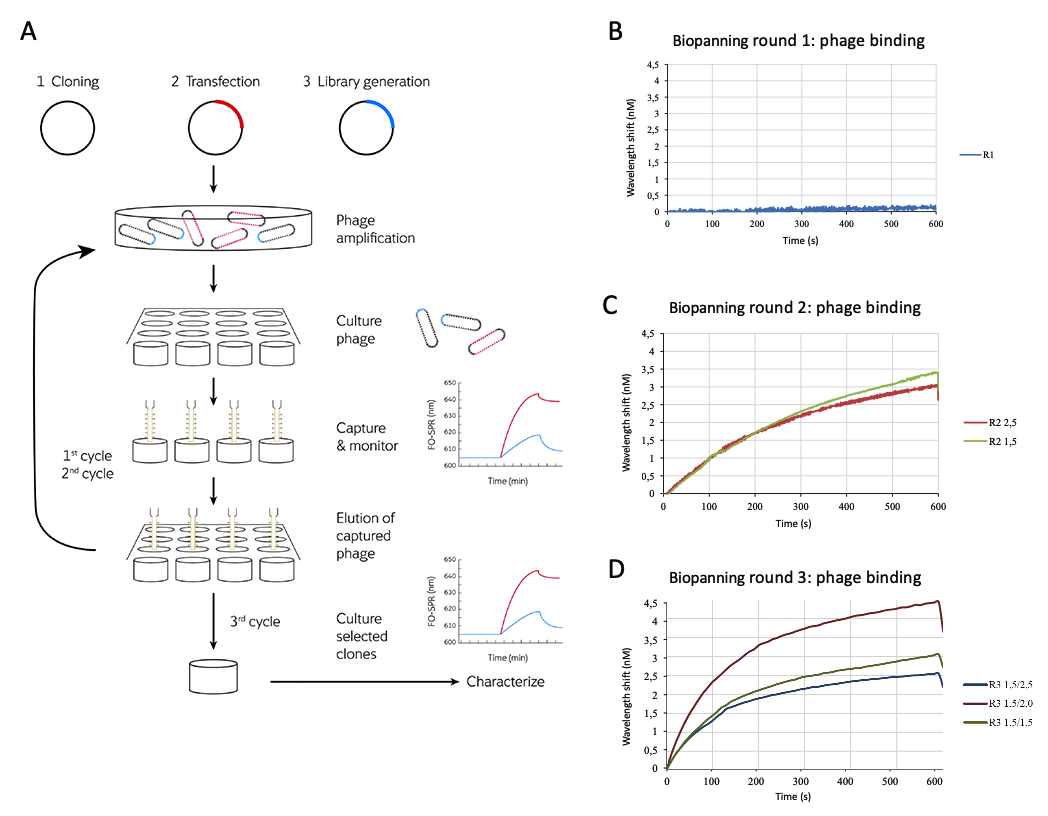
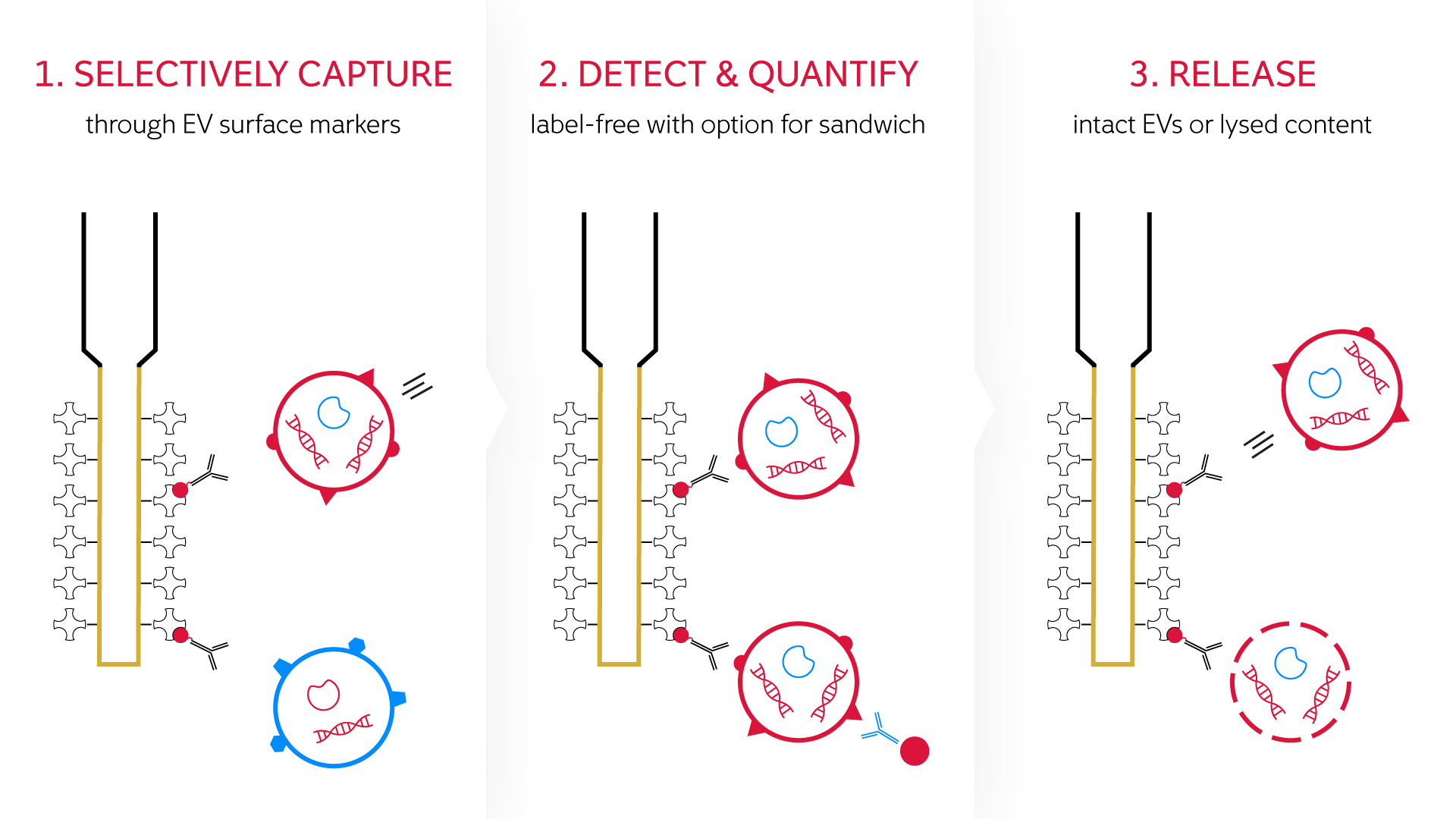
Biopanning is a technique used to select peptides or antibodies that bind to a target of interest using affinity selection. Phage are engineered to display a peptide of interest and captured by conjugating to a desired target.
The fiber-optic probes of WHITE FOxTM are ideally suited for this procedure. The user-friendly dip-in, fluidics-free setup offers a simple protocol for the binding, washing and elution steps, and the binding affinity, association and dissociation kinetics of the phage can be measured in real time. Unbound phage are washed from the surface and, finally, the bound phage are eluted to obtain the desired high-affinity phage clones which can then be used to create further display libraries.